The H-index is an index that takes into account the number of publications and the number of citations of an author or institution. The index measures the number of publications cited the same number of times or more. The value of the index depends on two factors: the number of publications and their popularity.
EXAMPLE: h=10 means that the author has 10 publications cited at least 10 times.
The Hirsch index is calculated on the basis of data from a specific database, so the index values may be different in each database.
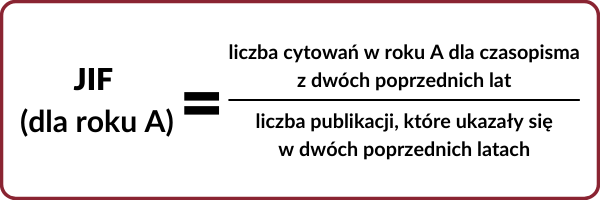
IF is the impact factor of a journal. The IF value for a given year is calculated as the ratio of the number of citations in that year for publications that appeared in the two previous years to the number of publications that appeared in the two previous years. It is calculated once a year for journals indexed in the Journal Citation Reports (JCR) database created by Clarivate Analytics.
Journals and conference proceedings included in the Web of Science Core Collection are taken into account.
The IF index is not standardised – it does not take into account differences between disciplines – so it cannot be used to compare journals from different disciplines.
The IF value can be checked in the Journal Citation Reports database on the Web of Science platform.
5-Year Journal Impact Factor
This is an impact factor that allows a journal to be assessed by its citability over a longer period of time. The principle of the calculation is the same as for the IF, but the last five years are taken into account instead of two years as in the case of the IF.
This is a measure of a journal's citability. The principle of its calculation is similar to the IF – the number of citations is related to the number of papers in that journal. The difference is the time span – for a given year, a period of four years is taken into account: the year in question plus the three preceding years – and the type of documents considered (these include peer-reviewed articles as well as editorial notes or letters to the editor).
The Cite Score is an indicator available in Scopus, and therefore journals indexed in Scopus are taken into account in the calculation of its value.
This index, like the IF, is not standardised – it should only be used to compare journals within a discipline.
The CiteScore Tracker, which is updated monthly, is used to track a journal's citation rate in a given year.
SCImago Journal Rank (SJR) is a coefficient that determines the prestige of a journal. The higher the value of this index, the greater the recognition and visibility of the journal. The SJR is calculated on the basis of journals indexed in the Scopus database.
The SJR is based on the assumption that citations are not equal. Therefore, citations from journals in the same or related discipline are given more weight than those from journals in other subject categories – this increases the likelihood that they are legitimate citations.
In calculating this index, the average number of citations of a journal over the last three years is determined in relation to the number of papers in that journal over the same period. In addition, the citation value is taken into account by the SJR of the journals from which these citations originate – the more citations from journals with a high SJR, the higher the SJR of the title will be.
Although the subject category of the journal is taken into account for the calculation of the SJR, this index is not standardised. Therefore, journals from different disciplines cannot be compared in terms of SJR value.
Source Normalized Impact per Paper (SNIP) is a measure of a journal's impact in a discipline. The calculation of the measure takes into account the average citation frequency of a given year for publications from the previous three years in relation to the citation potential of the discipline the journal represents (available from Database Citation Potential). The "maturation" time of the publication, i.e. the time elapsed between publication and the peak of citations, is also taken into account. Only original, review and conference articles indexed in the Scopus database are considered.
The SNIP is the only standardised indicator that allows the citation rate of a journal in a given category to be determined. Therefore, when using it, it is possible to compare journals from different disciplines.